[ad_1]
WISCONSIN — Wisconsin schools are seeing a “troubling increase” in chronic absenteeism amid the pandemic, according to a new report from the Wisconsin State Policy Forum.
This report examines the 2020-21 school year as COVID-19 ravaged the United States
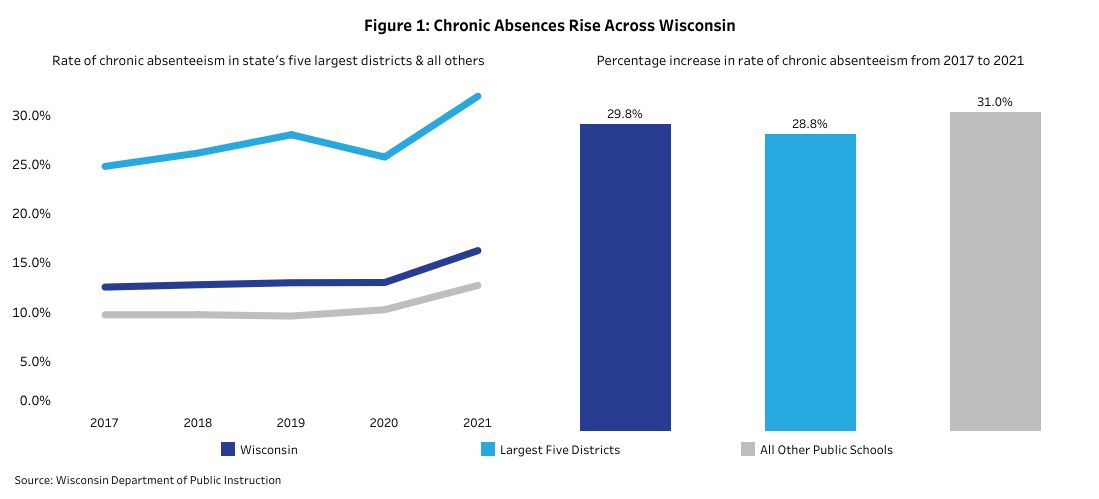
We found that the number of chronically absent students in Wisconsin public schools increased 3.7% from 2017 to 2021, from 12.4% to 16.1%.
The Wisconsin Policy Forum attributed this increase to a chronic increase in absenteeism during this period and a decline in overall student enrollment. Chronically absent students increased by 23.9% while the number of enrolled students decreased by 4.5%.
Most concerning to the researchers, absenteeism was highest in schools with high numbers of low-income students and students of color.
The researchers call these findings “additional threats to efforts to close the state’s long-standing academic achievement gap for these K-12 students.”
(Courtesy of Wisconsin Policy Forum via Wisconsin DPI)
But what is absenteeism?
According to the Wisconsin State Police Forum, since 2019, “chronic absenteeism” in Wisconsin means that a student spends 10% or more of their available school days, including both legitimate and truant absences. means absent. For a student to count towards this count, she must be enrolled for at least 90 days of the academic year.
However, figures reported from 2021 are cautionary as the definition of absenteeism was inconsistent across the pandemic. Researchers at the Wisconsin Policy Forum say that’s because the guidelines for taking attendance that year were often not strict or varied from district to district.
For example, in a virtual school environment, students may be considered present just by being there, or they may be required to actively participate in class. It may have been underestimated due to these different policies.
Despite this, there were still many reports of absenteeism at school. Most of the increase came from the state’s largest school district, where he reported an absenteeism rate of 31.8% in 2021, compared to other school districts and schools where he had an absenteeism rate of 12.6%.
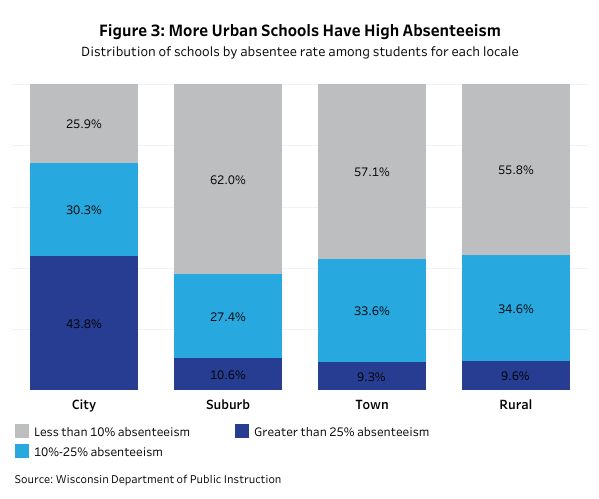
Compared to 2017, the largest school district’s chronic absentee rate increased by 28.8% in 2021. Over the same period he was up 31%. Absence rates were also high in urban schools.
(Courtesy of Wisconsin Policy Forum via Wisconsin DPI)
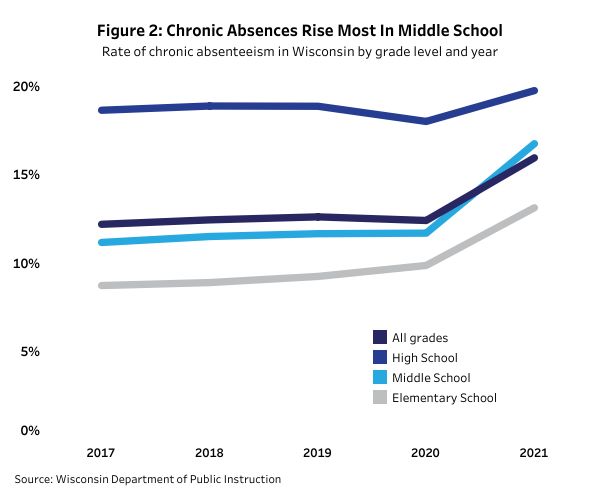
According to the Wisconsin State Policy Forum, Wisconsin high school students consistently have high absentee rates. However, in 2021, absenteeism among young students has increased. Junior high school students had the largest increase, rising from 11.7% to 16.7%.
The most surprising point was that absenteeism was higher in schools with disadvantaged groups. A study by the Wisconsin State Policy Forum found that schools with over 25% absenteeism had higher rates of low-income students (69.1%) or non-white students (62%).
Looking at schools with less than 5% absenteeism, the number of disadvantaged students decreased.
The same was true for schools with many students with disabilities. Students with an identified disability accounted for 17.9% of her students in schools with over 25% absenteeism, but only 2.4% in schools with less than 5% absenteeism.
This is especially important given that chronic absenteeism has been shown to negatively impact student performance, student mental health, dropout rates, and adulthood overall.
(Courtesy of Wisconsin Policy Forum via Wisconsin DPI)
Researchers say the rising trend in absenteeism is similar to what’s happening across the country. They pointed to state reports that estimated the number of chronically absent students may have doubled nationally compared to pre-pandemic levels.
However, they said, “It is still unclear whether the increase was a temporary pandemic-related spike.”
An official at the Wisconsin State Policy Forum said statewide intervention may be needed to address the problem “before it becomes unsolvable.”
They also suggested that school districts may want to consider expanding after-school tutoring and summer school to make up for lost learning.
The group said new statewide data for 2022 will be released this spring.
[ad_2]
Source link

