[ad_1]

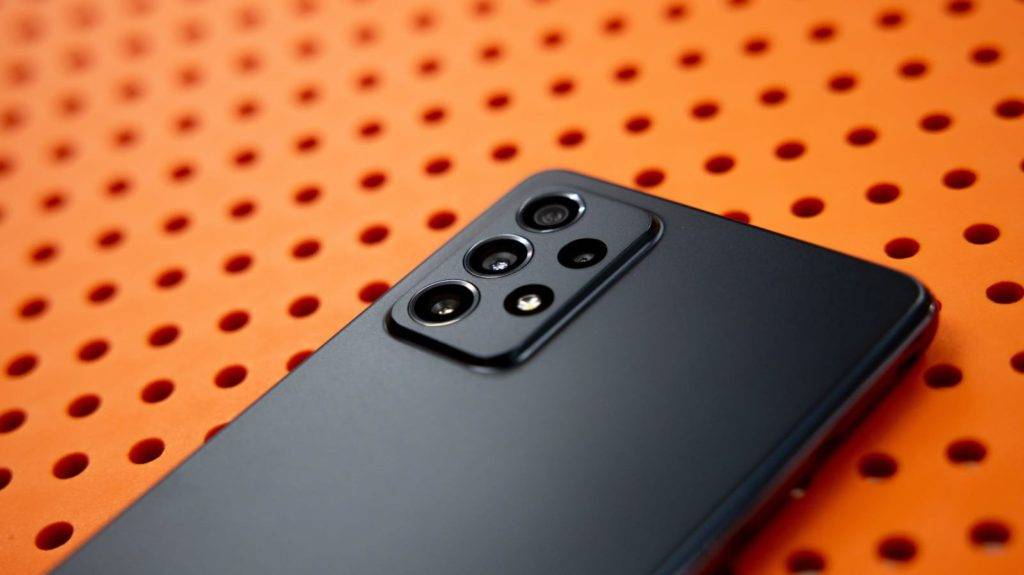
Two vulnerabilities in the Galaxy App Store, the official repository for Samsung devices, allow attackers to install arbitrary apps on the Galaxy Store without the user’s knowledge or direct victims to malicious websites. There is likely to be.
This issue was discovered by NCC Group researchers between November 23rd and December 3rd, 2022.
The South Korean smartphone maker announced on January 1, 2023 that it fixed two flaws and released a new version (4.5.49.8) of the Galaxy App Store.
Today, the NCC group released technical details of two security issues, as well as proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for each.
Note that both attacks require local access. This is a no-brainer for aspiring hackers and malware distributors targeting mobile devices.
Force app installation on Android
The first of the two flaws, tracked as CVE-2023-21433, is improper access controls that allow an attacker to install any application available on the Galaxy App Store.
The NCC has discovered that the Galaxy App Store does not handle incoming intents in a secure manner, allowing apps on the device to send arbitrary app install requests.
The PoC shared by NCC analysts installs the ‘Pokemon Go’ game in the app component by sending the ‘ADB’ (Android Debug Bridge) command with the intent of the specified target application to the app store. to do so.

Intents can also specify whether to open the new application after installation. This gives attackers more options on how to conduct their attacks.
The second vulnerability, CVE-2023-21434, is improper input validation that allows an attacker to execute JavaScript on the targeted device.
NCC researchers discovered that the Galaxy App Store web view contains a filter that limits the domains that can be viewed. However, that filter is not configured properly and bypassing it allows him to force the webview to access malicious domains.
The PoCs shown in the report are hyperlinks that, when clicked from Chrome, open a page containing malicious JavaScript and run on your device.
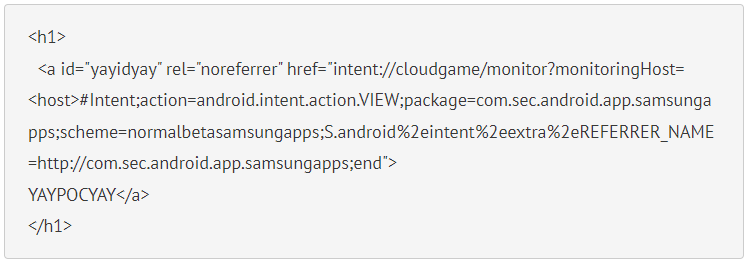
The NCC explains that the only prerequisite for this attack is that the malicious domain contains the “player.glb.samsung-gamelauncher.com” part. An attacker can register any domain and add parts of it as subdomains.
Impact on Samsung users
Running arbitrary JavaScript code in a web view from within a system-permissions app, such as Galaxy Store, can have serious security implications.
Depending on the attacker’s motives, an attack could lead to manipulation of the app UI, access to sensitive information, or even crashing the app.
Installing and auto-starting apps from the Galaxy store without the user’s knowledge can lead to data and privacy compromises, especially if an attacker has previously uploaded a malicious app to the Galaxy store.
It’s important to note that CVE-2023-21433 cannot be exploited on Samsung devices running Android 13, even if you’re using an older, vulnerable version of the Galaxy Store. This is due to additional security protections in the latest version of Google’s mobile OS.
Unfortunately, all Samsung devices that are no longer supported by their vendors and remain on older versions of the Galaxy Store are vulnerable to two vulnerabilities discovered by NCC Group researchers.
[ad_2]
Source link

