[ad_1]
Teachers worried about students submitting essays written by popular artificial intelligence chatbots have a new tool of their own.
Edward Tian, 22, a senior at Princeton University, created an app that detects if text is written by ChatGPT. ChatGPT is a viral he chatbot that has raised concerns for its possible unethical use in academia.

/ Edward Tian
/
Edward Tian
A computer science major with a minor in journalism, Tian spent part of his winter break building GPTZero. GPTZero can “quickly and efficiently” decipher whether a human wrote the essay or he ChatGPT wrote the essay, he said.
His motivation for creating the bot was to combat the rise of AI plagiarism and what he sees. Since the release of his ChatGPT in late November, there have been reports of students using groundbreaking language models to submit AI-generated assignments as their own.
“Chatgpt hype is rife. Is this written by AI? We humans deserve to know!” Tian wrote in a tweet Introducing GPTZero.
After releasing his bot online on Jan. 2, Tian said many teachers have reached out to him to tell them about the positive results they’ve gotten from the tests.
Over 30,000 people have tried GPTZero within a week of launch. It was so popular that the app crashed. Streamlit, the free platform that hosts GPTZero, has stepped in to support Tian with more memory and resources to handle web traffic.
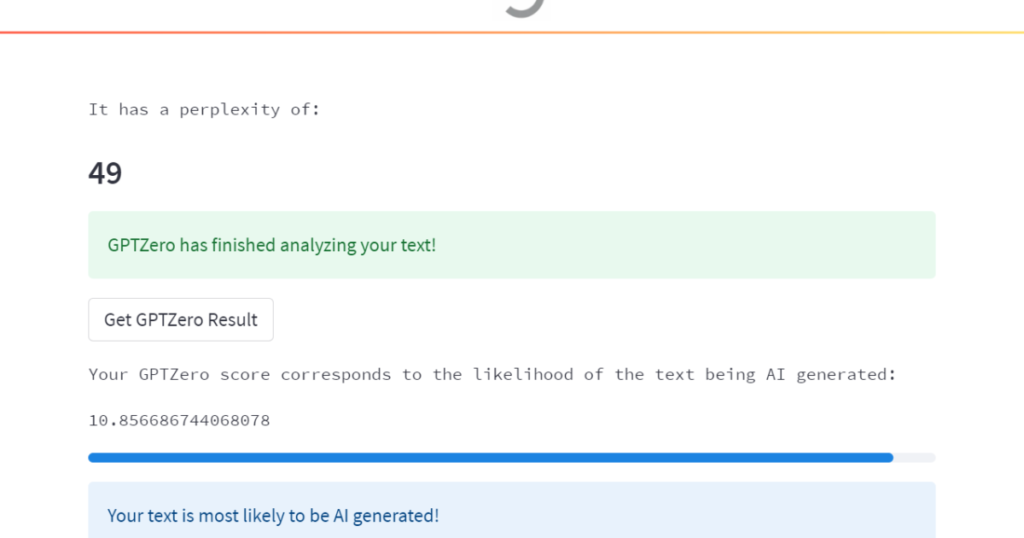
How GPTZero Works
To determine if a snippet was written by a bot, GPTZero uses two metrics: ’embarrassment’ and ‘burstyness’. Perplexity measures the complexity of the text. If GPTZero is confused by the text, it’s highly likely that the text is very complex and was written by a human. However, if the text is more friendly to the bot because it was trained on such data, it will be less complex and more likely to be generated by AI.
Apart from that, burstiness compares sentence variations. Humans tend to be more bursty, for example writing long or complex sentences alongside short sentences. AI sentences tend to be more uniform.
In a demonstration video, Tian compared how apps analyze stories. New Yorker LinkedIn post written by ChatGPT. We succeeded in distinguishing between human handwriting and AI handwriting.
Tian admitted that his bot is not foolproof, as some users reported when testing the bot. He said he is still working to improve the model’s accuracy.
But the tools help Tian work towards its core mission of bringing transparency to AI by designing apps that shine a light on what separates humans from AI.
“For a long time, AI was a black box where you didn’t really know what was going on inside,” he said. “And he was GPTZero and I wanted to push it back and start fighting.”
The quest to stop AI plagiarism
College seniors aren’t the only ones racing to stop AI plagiarism and counterfeiting. ChatGPT developer OpenAI promised to prevent AI plagiarism and other malicious applications. Last month, Scott Aaronson, a researcher at OpenAI who currently focuses on AI safety, said the company had “watermarked” his GPT-generated text with “discreet covert signals” to We’ve made it clear that we’re working on ways to identify its source.
Hugging Face, an open-source AI community, has published a tool to detect if text was created by GPT-2, the previous version of the AI model used to create ChatGPT. A South Carolina philosophy professor who happened to know about the tool said he used it to catch students submitting work written in AI.
The New York City Department of Education announced Thursday that it will block access to ChatGPT on school networks and devices, citing “negative effects on student learning and concerns about the safety and accuracy of the content.”
Tian is not against using AI tools like ChatGPT.
GPTZero “is not a tool to discourage the use of these technologies,” he said. “But with any new technology, we need to be able to adopt it responsibly, and we need safeguards.”
Copyright 2023 NPR. For more information, please visit https://www.npr.org.
[ad_2]
Source link